The edible oil refining process in general comprises of Degumming, Neutralization, Bleaching and Deodorization and Winterisation. Chemical refining is the traditional method whereby the free fatty acid of the crude oils are neutralized with Caustic Soda. The resultant Sodium Soaps are removed by Batch Settling or by means of Centrifugal Separators. The neutral oils are subsequently bleached and deodorized. This method can be used for reliably refining virtually all crude oils, including oils of low quality, with the exception of Castor Oil.
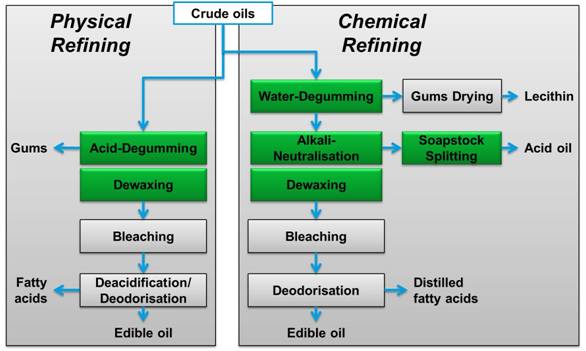
In all alternative method of edible oil refining of Physical refining, the free fatty acids are removed by distillation in one stage of deodorizing. A fundamental criterion for using this method is that the crude oils should be degummed as effectively as possible, however this is only possible to a limited extent with some crude oil qualities. Other oils for instance cottonseed oil or fish oils, are fundamentally not suitable for Physical Refining.
Two processes have been developed for the refining of edible oils and fats, i.e. physical and chemical refining; the decision which process to use depends on the types and qualities of the crude oil to be processed. The names physical and chemical refining come from the process technology used to remove the Free Fatty Acids (FFA) that are responsible for the oil acidity.
Physical refining is a process making use of the lower boiling point of the FFA compared to the boiling point of the triglyceride oil. Chemical refining is the traditional method used in past centuries. The main purpose of chemical refining is to saponify the FFA by an alkaline solution and dilute the resulting soaps in a water phase. These soaps are removed by separators. For small scale batch processes static separation is used but for continuous processing and large scale processes, centrifugal separation is used. The neutral oils are subsequently bleached and deodorised. This chemical refining can be used for reliably refining virtually all crude oils, including oils of low quality, with the exception of castor oil.

